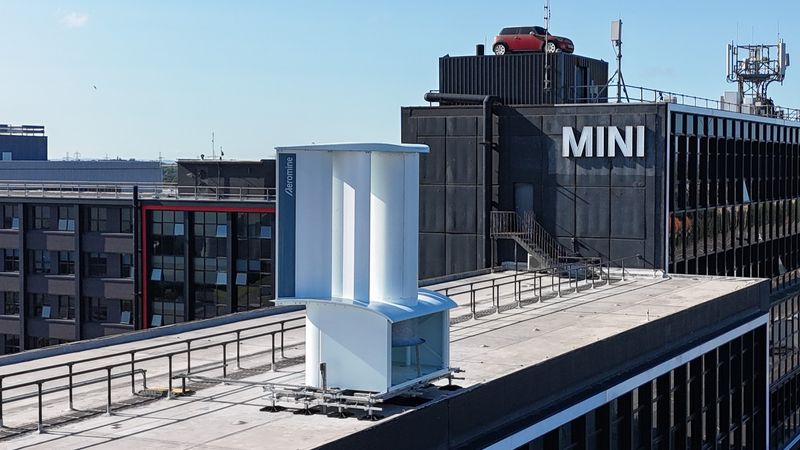
The MINI plonked on top of a BMW manufacturing plant in Oxford, England is no longer the only unusual sight meeting passersby; it’s now been joined on the roof by the UK’s first “motionless” wind energy system.
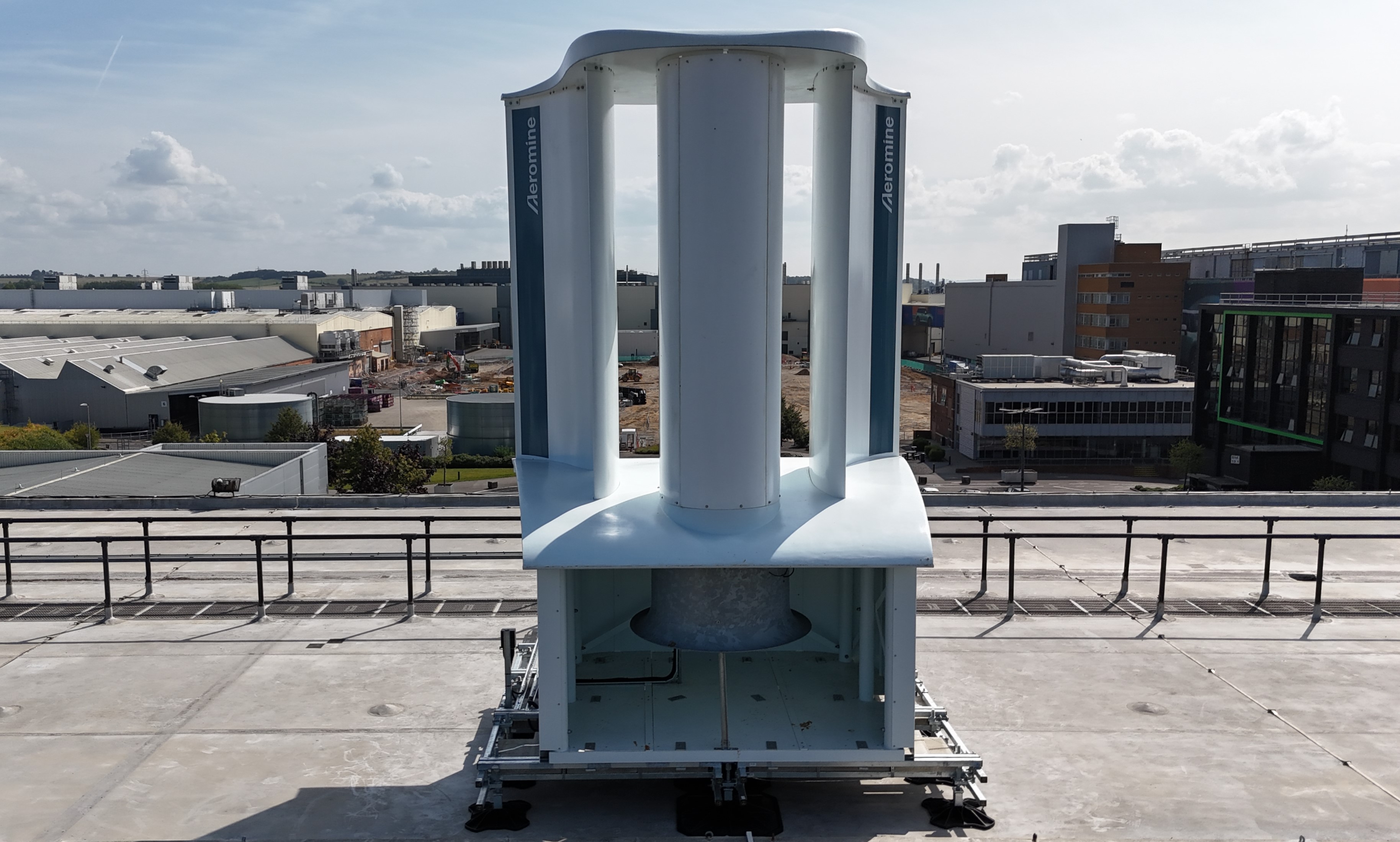
Designed by the company Aeromine Technologies, the unit doesn’t exactly look like your traditional wind turbine – no big blades in sight. Instead, it has a large central column and vertical airfoils, the kind of curved structure that you see in airplane wings.
This design is intended to create a vacuum effect. With the unit placed on the edge of a building and oriented towards the prevailing wind, according to Aeromine, the design accelerates the wind flowing into the unit even further, which creates a region of low pressure behind the column seen in the middle.
As a result, the air is pulled through the bottom of the unit, where there’s a propeller, which – much like a regular wind turbine – spins a generator, and shazam, you’ve got yourself some electricity.

The installation of the turbine on BMW’s roof is part of the company’s aim to reduce its carbon footprint, which has already seen solar panels placed across the site. While that project has seen success, the problem is that it’s not quite so sunny in the UK during the winter months, nor, for hopefully obvious reasons, in the evening.
However, those times do happen to be fairly windy, which is what the unit is designed to capitalize on. “Our 'motionless' wind energy technology is designed to work seamlessly alongside solar systems, maximising the renewable energy output from rooftops,” said Aeromine’s managing director Claus Lønborg in a statement.
According to Lønborg, the turbine’s bladeless design could also help to “address challenges like noise [and] vibrations” but may further act as a potential solution to a problem long associated with traditional wind turbines: their impact on wildlife, and primarily, birds.
Although it’s thought to be a relatively small number of birds killed by wind turbines each year in comparison to say, hungry housecats, or flying into buildings, it’s still very much a concern, particularly if vulnerable species are involved.
The “motionless” wind turbine might be one answer, but there are plenty of existing wind farms out there, and it would be far from cheap to tear them all down and replace them. Others looking to make turbines safer have had to get creative with what they already have – whether that’s by making turbine blades stripy, or adding giant bird boxes.